1. Protect Sensitive Data
Microsoft 365 often contains sensitive information (internal documents, customer information, personal data). An audit helps ensure that this data is properly protected against unauthorized access, misconfigurations, and external threats.
2. Access and Permission Control
In a Microsoft 365 environment, many users and services are interconnected. Auditing helps verify that access rights are properly configured, ensuring that only authorized users access sensitive information. It also helps validate that permissions are not excessively broad (principle of least privilege).
3. Threat Detection and Prevention
Microsoft 365 offers several built-in security tools, such as Microsoft Defender for Office 365 and suspicious sign-in monitoring. An audit evaluates the activation and effectiveness of these features, ensuring they are properly configured to detect and prevent threats such as phishing attacks or fraudulent sign-ins..
4. Compliance with Regulations and Standards
Businesses often need to comply with specific regulations (GDPR, HIPAA, etc.). A Microsoft 365 audit ensures that security, privacy, and data retention settings meet these requirements. In the event of an audit or incident, the organization will be able to demonstrate that it is taking the necessary compliance measures.
5. Device and Application Management
Microsoft 365 is accessible from multiple device types (computers, phones, tablets) and third-party applications, increasing the risk of data leakage. An audit evaluates device management (e.g. with Intune) and connected applications to ensure they comply with the organization’s security policies.
6. Configuring Security and Retention Policies
Microsoft 365 provides options for configuring security policies (such as password management, multi-factor authentication) and email and file retention policies. Auditing helps verify that these policies are appropriate for business needs and applied consistently.
7. Detection of Abnormal Behaviors and Violations
An audit examines activity logs and security reports to identify any abnormal behavior, such as unusual login attempts or access to sensitive documents outside of normal hours. This information helps detect potential breaches before they cause real damage.
8. Parameter Optimization and Cost Reduction
An audit can reveal unused or underutilized security features, allowing the organization to better optimize its settings or reduce licensing costs by disabling unnecessary options.
9. User Training and Awareness
Finally, a Microsoft 365 security audit highlights user training needs, including on security best practices, password management, phishing protection, etc. User awareness is often a critical barrier against cyber threats.
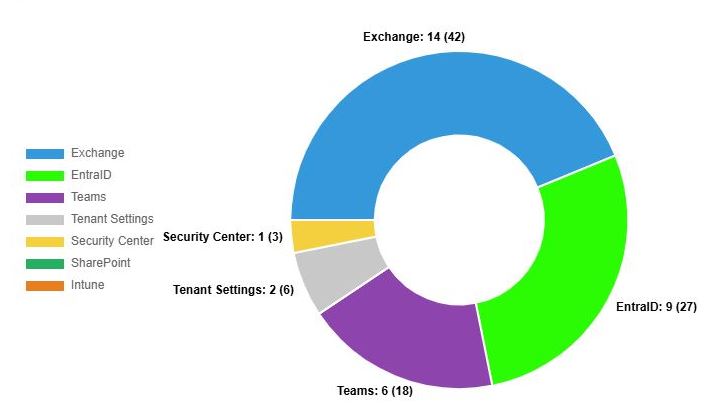

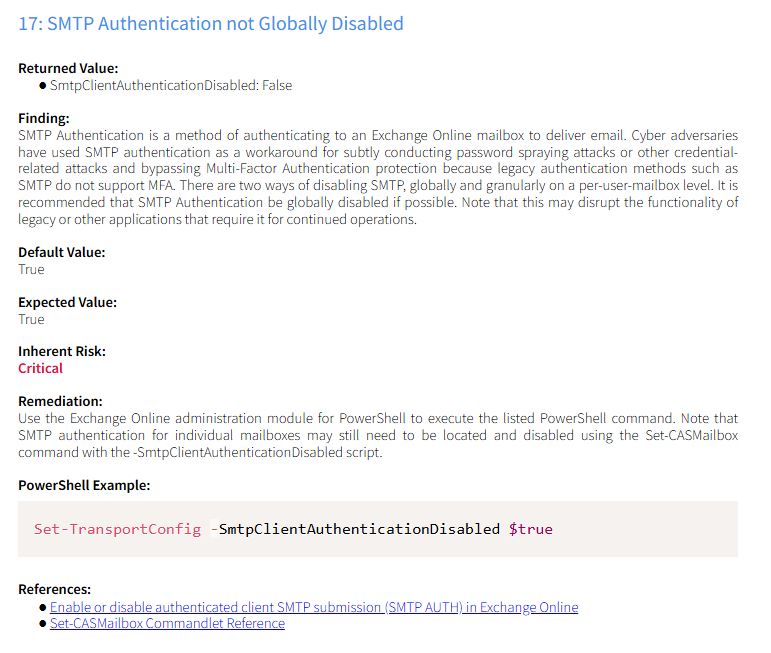
 m365-audit-securite.com
m365-audit-securite.com